
Add To Favorites
Why is this planet so dark? Planet TrES-2b reflects back less than one percent of the light it receives, making it darker than any known planet or moon, darker even than coal. Jupiter-sized TrES-2b orbits extremely close to a sun-like star 750 light years away, and was discovered producing slight eclipses in 2006 using the modest 10-cm telescopes of the Trans-Atlantic Exoplanet Survey (TrES). The alien world's strange darkness, however, was only uncovered recently by observations indicating its slight reflective glow by the Sun-orbiting Kepler satellite. An artist's drawing of planet is shown above, complete with unsubstantiated speculation on possible moons. Reasons for TrES-2b's darkness remain unknown and are an active topic of research.
2011-08-22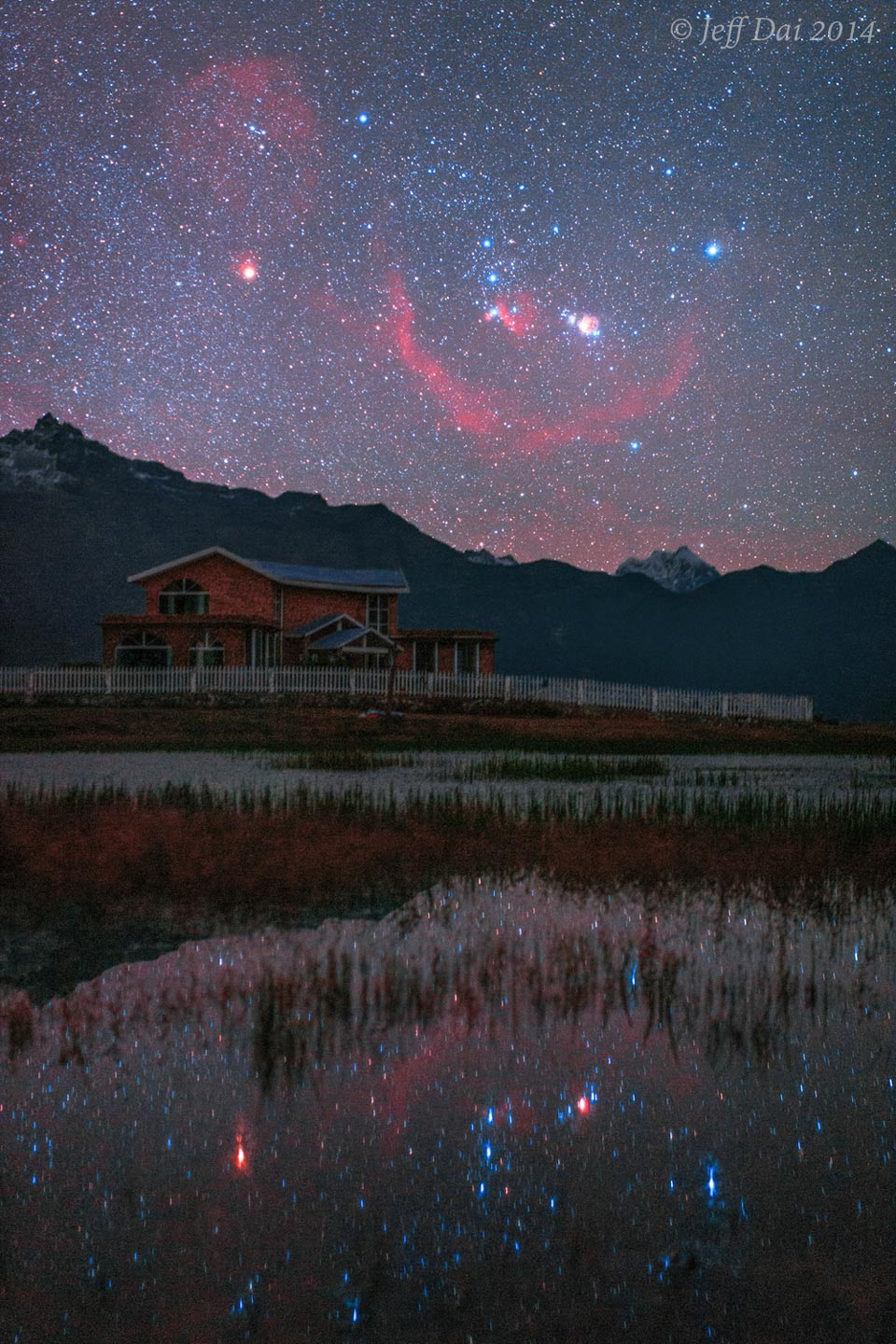
Add To Favorites
This night was so serene you could see Orion rise downwards. The unusual spectacle was captured in this single-exposure image, featuring a deep sky around the famous constellation of Orion that appeared both above -- and reflected in -- a peaceful lake in the Gyirong Valley of Tibet, China. Taken last year at this time, the three belt stars of Orion can be seen lined up almost vertically above and below the Himalayan Mountains. The complex Orion Nebula can be seen to the belt stars' right, while the red-glowing circular structure surrounding Orion is Barnard's Loop. Also, the bright red star Betelgeuse is doubly visible on the image left, while bright blue Rigel appears twice on the image right. Familiar Orion is becoming increasingly visible as Winter (Summer) descends on the Northern (Southern) hemisphere. Follow APOD on: Facebook, Google Plus, or Twitter
2015-10-05 Jeff Dai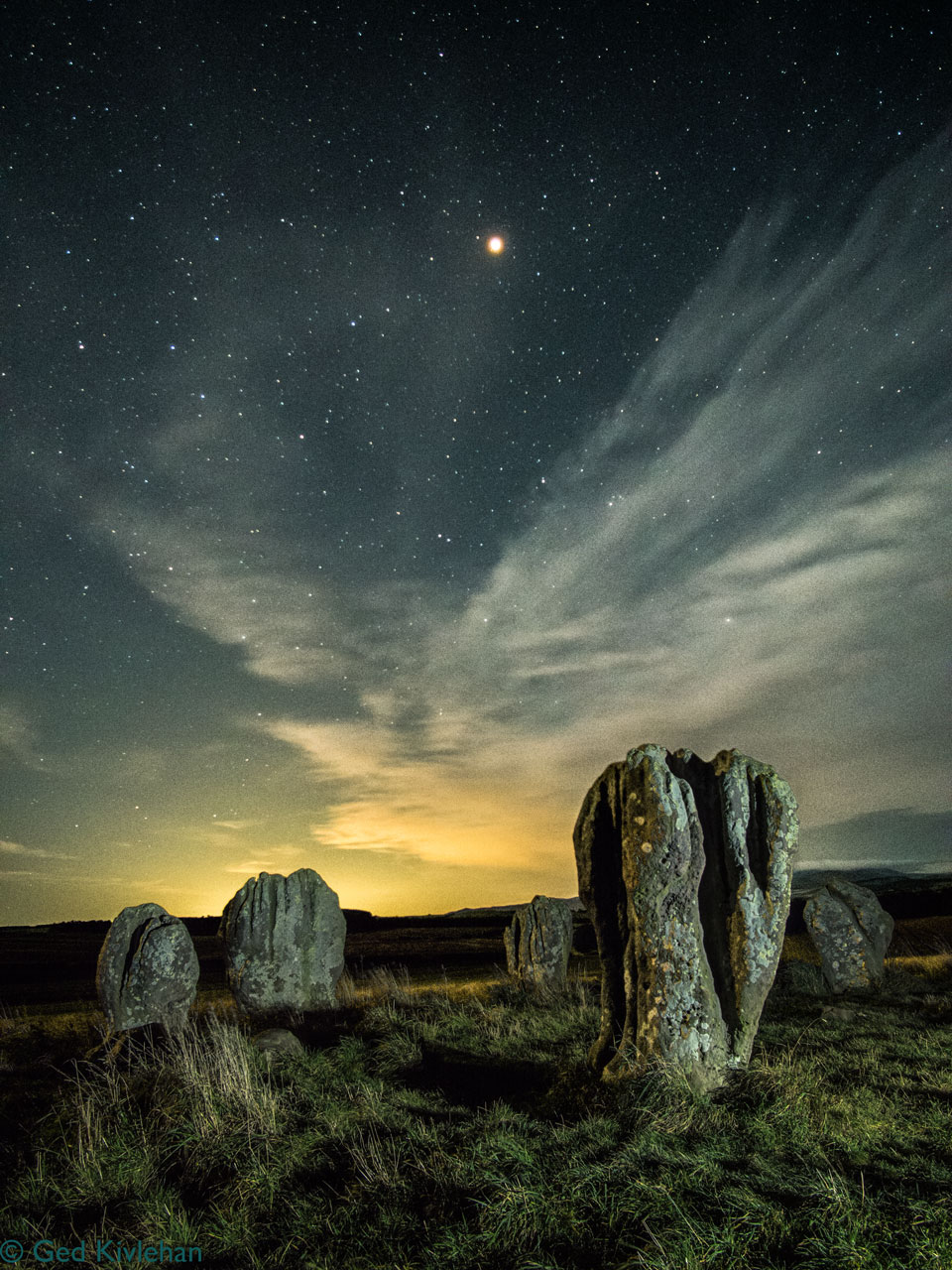
Add To Favorites
Why are these large stones here? One the more famous stone circles is the Duddo Five Stones of Northumberland, England. Set in the open near the top of a modest incline, a short hike across empty fields will bring you to unusual human -sized stones that are unlike anything surrounding them. The grooved, pitted, and deeply weathered surfaces of the soft sandstones are consistent with being placed about 4000 years ago -- but placed for reasons now unknown. The featured image -- a composite of two consecutive images taken from the same location -- was captured last October under a starry sky when the Earth was passing near Mars, making the red planet unusually large and bright. Mars remains visible at sunset, although increasingly close to the horizon over the next few months. APOD via Instagram in: English, Indonesian, Persian, and Portuguese
2021-03-23 Ged Kivlehan
Add To Favorites
NGC 6240 offers a rare, nearby glimpse of a cosmic catastrophe in its final throes. The titanic galaxy-galaxy collision takes place a mere 400 million light-years away in the constellation Ophiuchus. The merging galaxies spew distorted tidal tails of stars, gas, and dust and undergo fast and furious bursts of star formation. The two supermassive black holes in the original galactic cores will also coalesce into a single, even more massive black hole and soon, only one large galaxy will remain. This dramatic image of the scene is a composite of narrowband and near-infrared to visible broadband data from Hubble's ACS and WPC3 cameras, a view that spans over 300,000 light-years at the estimated distance of NGC 6240.
2015-05-21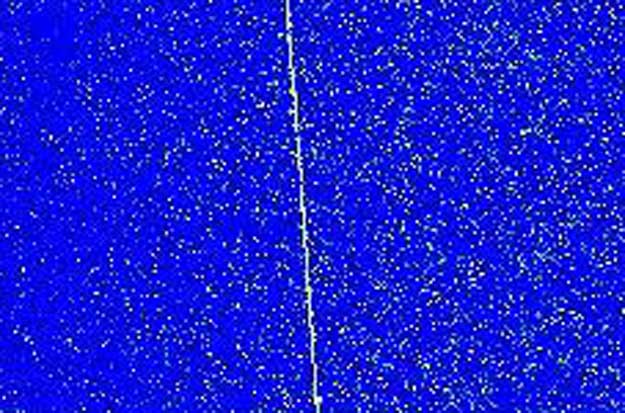
Add To Favorites
No one knows for sure what caused this signal. There is a slight possibility that it just might originate from an extraterrestrial intelligence. The bright colors on the blue background indicate that an anomalous signal was received here on Earth by a radio telescope involved in a Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI). A search for these signals is ongoing by several groups including volunteer members of the SETI League. Time labels the vertical axis of the above plot, and frequency marks the horizontal axis. Although this strong signal was never positively identified, astronomers have identified in it many attributes characteristic of a more mundane and ultimately terrestrial origin. In this case, a leading possibility is that the signal originates from an unusual modulation between a GPS satellite and an unidentified Earth-based source. Many unusual signals from space remain unidentified. No signal has yet been strong enough or run long enough to be unambiguously identified as originating from an extraterrestrial intelligence.
2002-07-28 SETI League
Add To Favorites
This Hubble Space Telescope image of a group of faint galaxies "far, far away" is a snap shot of the Universe when it was young. The bluish, irregularly shaped galaxies revealed in the image are up to eight billion light years away and seem to have commonly undergone galaxy collisions and bursts of star formation. Studying these objects is difficult because they are so faint, however they may provide clues to how our own Milky Way Galaxy formed.
1995-09-07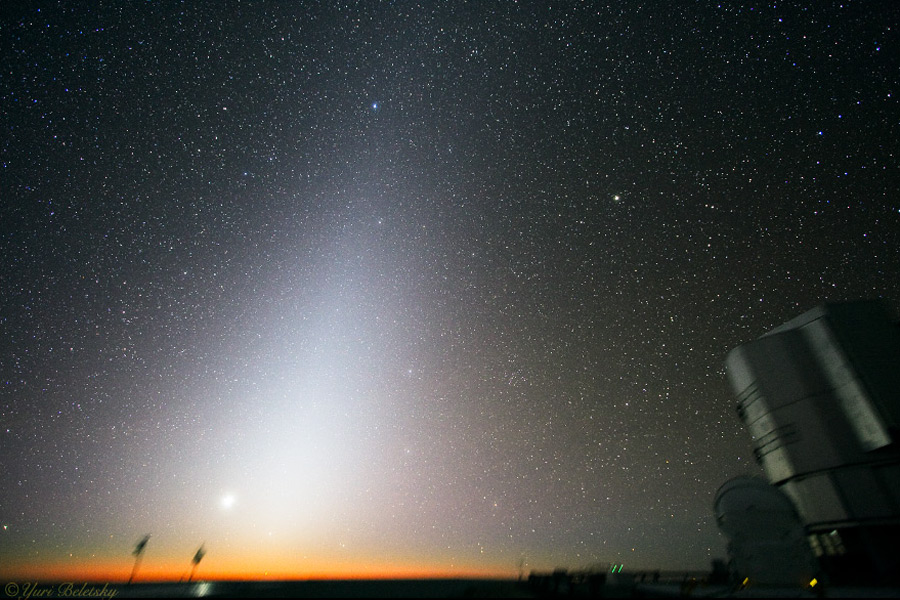
Add To Favorites
An unusual triangle of light will be particularly bright near the eastern horizon before sunrise during the next two months for observers in Earth's northern hemisphere. Once considered a false dawn, this triangle of light is actually Zodiacal Light, light reflected from interplanetary dust particles. The triangle is clearly visible toward the left of the frame taken from the Paranal Observatory in Chile in July. Zodiacal dust orbits the Sun predominantly in the same plane as the planets: the ecliptic. Zodiacal light is so bright this time of year because the dust band is oriented nearly vertical at sunrise, so that the thick air near the horizon does not block out relatively bright reflecting dust. Zodiacal light is also bright for people in Earth's northern hemisphere in March and April just after sunset. APOD editor to review best space pictures in Philadelphia tomorrow (Wednesday) night
2007-09-25 Yuri Beletsky (ESO)
Add To Favorites
It was the strongest gravitational wave signal yet measured -- what did it show? GW250114 was detected by both arms of the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory (LIGO) in Washington and Louisiana USA earlier this year. Analysis showed that the event was created when two black holes, each of mass around 33 times the mass of the Sun, coalesced into one larger black hole with a mass of around 63 solar masses. Even though the event happened about a billion light years away, the signal was so strong that the spin of all black holes, as well as initial ringing of the final black hole, was deduced with exceptional accuracy. Furthermore, it was confirmed better than before, as previously predicted, that the total event horizon area of the combined black hole was greater than those of the merging black holes. Featured, an artist's illustration depicts an imaginative and conceptual view from near one of the black holes before collision.
2025-09-24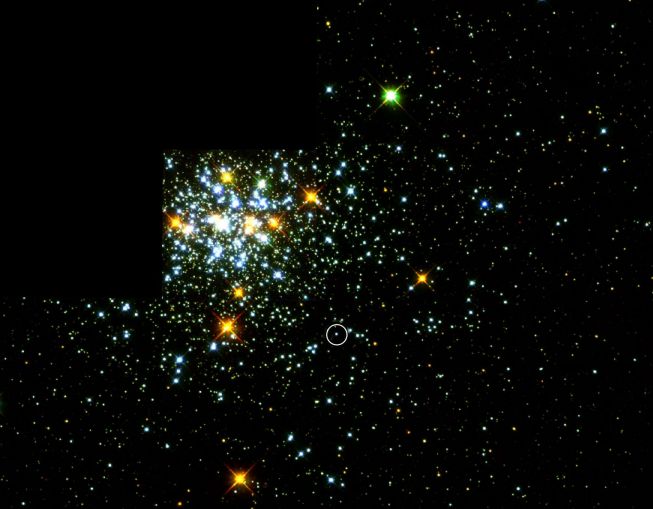
Add To Favorites
This is NGC 1818, a youthful, glittering cluster of 20,000 stars residing in the Large Magellanic Cloud, 180,000 light-years away. Pick a star. Any star. Astronomers might pick the unassuming bluish-white one (circled) which appears to be a hot newly formed white dwarf star. What makes it so interesting? The standard astronomical wisdom suggests that stars over 5 times as massive as the sun rapidly exhaust their nuclear fuel and end their lives in a spectacular supernova explosion. With less than this critical mass they evolve into red giants, pass through a relatively peaceful planetary nebula phase, and calmly fade away as white dwarf stars like this one. Except that as a member of the NGC 1818 cluster, this new white dwarf would have evolved from a red giant star over 7.6 times as massive as the sun -- which should have exploded! Its discovery will likely force astronomers to revise the limiting mass estimate for supernovae upward.
2003-05-31
Add To Favorites
On March 14 the Moon was Full. In an appropriate celebration of Pi day, that put the Moon 3.14 radians (180 degrees) in ecliptic longitude from the Sun in planet Earth's sky. As a bonus for fans of Pi and the night sky, on that date the Moon also passed directly through Earth's umbral shadow in a total lunar eclipse. In clear skies, the colors of an eclipsed Moon can be vivid. Reflecting the deeply reddened sunlight scattered into Earth's shadow, the darkened lunar disk was recorded in this time series composite image from Cerro Tololo Observatory, Chile. The lunar triptych captures the start, middle, and end of the total eclipse phase that lasted about an hour. A faint bluish tint seen just along the brighter lunar limb at the shadow's edge is due to sunlight filtered through Earth's stratospheric ozone layer. Growing Gallery: Total Lunar Eclipse of 2025 March
2025-03-15 Petr Horálek